Measurements of energy expend iture
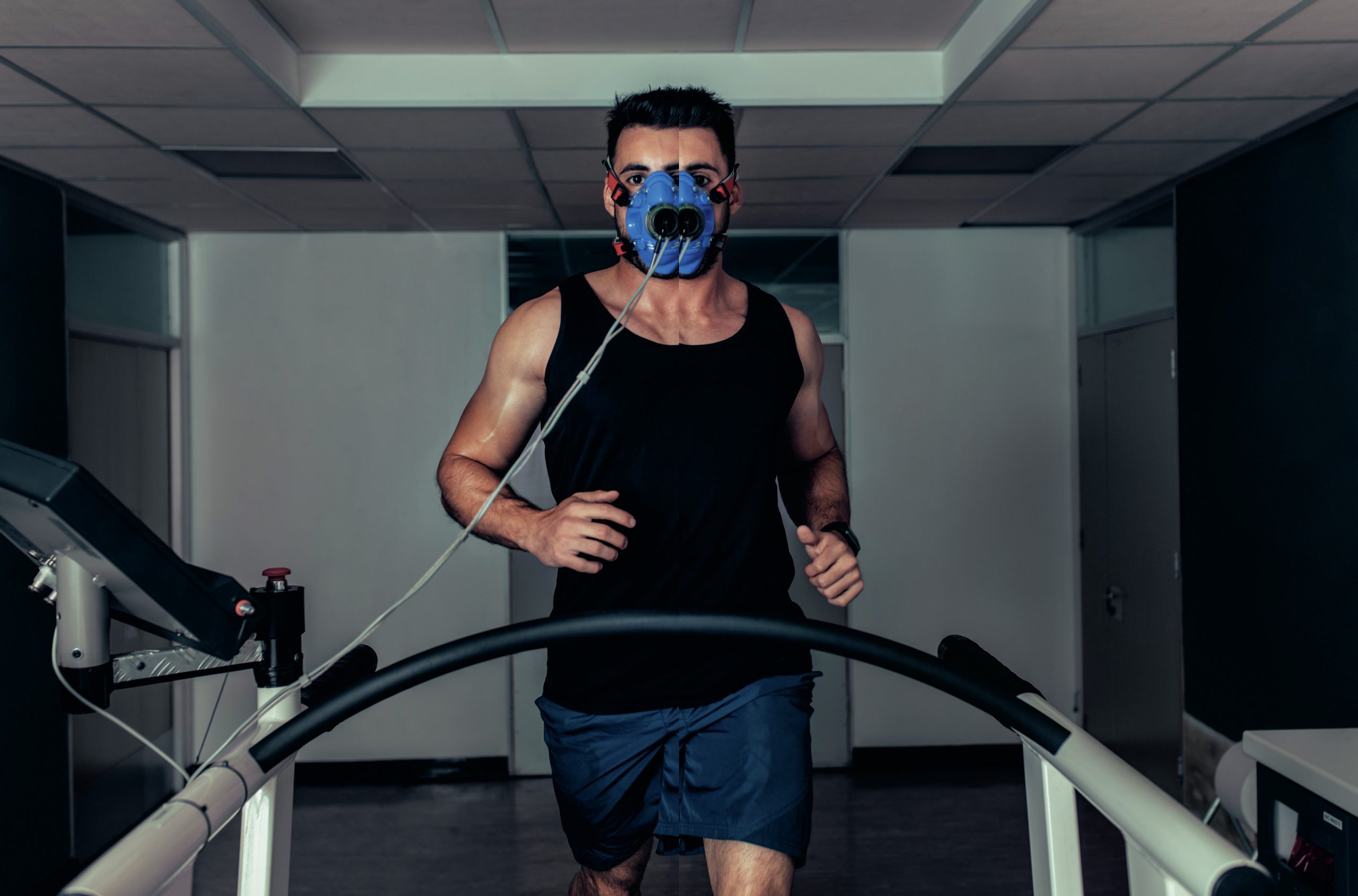

Indirect calorimetry
Indirect calorimetry measures how much carbon dioxide is produced and how much oxygen is consumed at both rest and during aerobic exercise. Calculating the gas volumes also enables us to find out the main substrate being used (fat or carbohydrate).
VO2 max
There are many tests that can evaluate VO2 max. The most common one is the multistage fitness test or more commonly called ‘bleep test’. Here the individual performs a 20-metre progressive shuttle run to a bleep, until they reach complete exhaustion. The level that is reached can be compared with a standard results table. Other tests include the Harvard step test and the Cooper 12-minute run, but all of these only give an indication or prediction of VO2 max. A sports science laboratory can produce much more valid and reliable results using direct gas analysis.
Lactate sampling
Lactate sampling involves taking a tiny blood sample and a handheld device analyses the blood and indicates how much lactate is present. This is an accurate and objective measure of the level of lactate in the blood. It can also be used as a means of measuring exercise intensity and gives an idea of level of fitness.
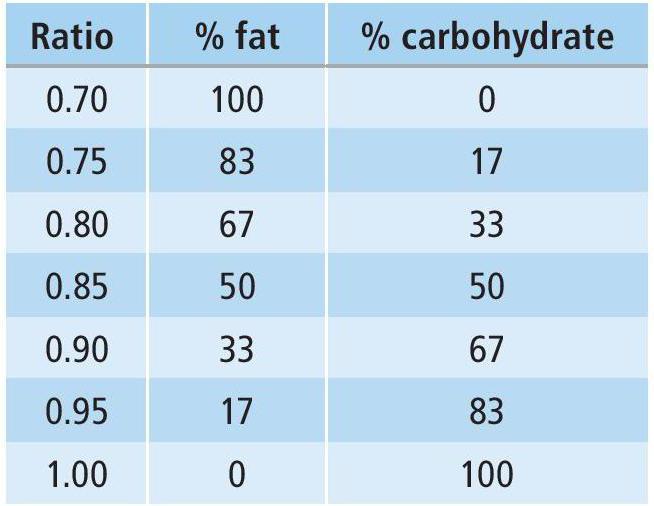
Respiratory exchange ratio
Measuring the respiratory exchange ratio (RER) requires an athlete to be attached to a gas analyser while on a treadmill or cycle ergometer so that accurate readings can be taken on the amount of carbon dioxide produced compared to oxygen consumed. RER calculates energy expenditure and provides information about the use of fats and carbohydrates during exercise. The calculation determines which energy sources are being oxidised and hence whether the performer is working aerobically or anaerobically. The table below shows the percentage of fats and carbohydrates used from the RER.
PEReviewExtras
Download this poster at www.hoddereducation.co.uk/pereviewextras





