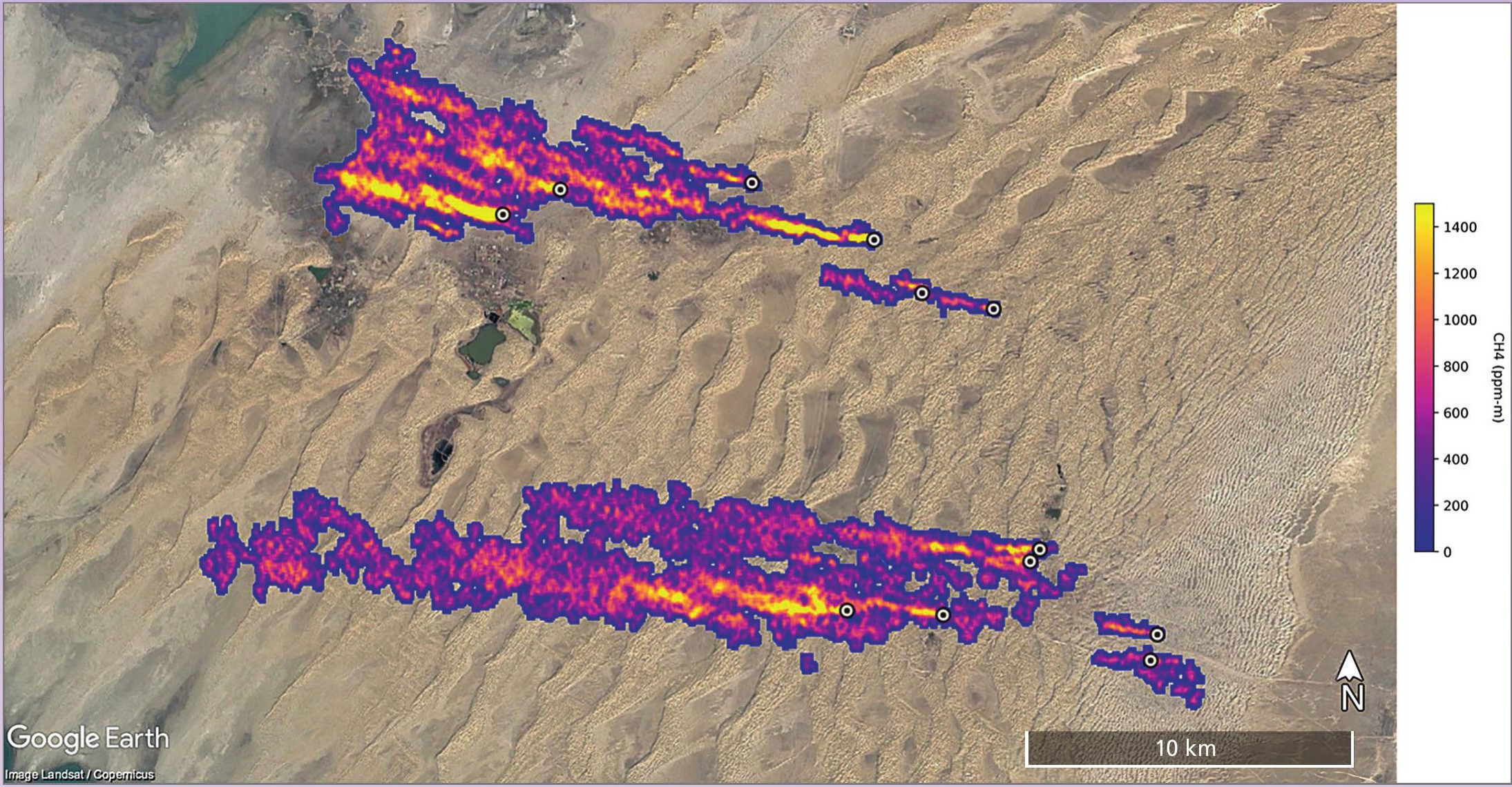
Methane (CH4) is a potent greenhouse gas which, over the 20 years after its release into the atmosphere, has more than 80 times the global warming potential of carbon dioxide (CO2). The aims of the Paris Agreement cannot be achieved without cutting global methane emissions by some 40% to 45% by 2030.
Agriculture is the largest source of anthropogenic methane emissions (40%), with the energy sector (oil and gas) accounting for about 35%. The methane released during fossil fuel extraction has been targeted because emissions in this sector can be reduced rapidly with the least cost.
Your organisation does not have access to this article.
Sign up today to give your students the edge they need to achieve their best grades with subject expertise
Subscribe




