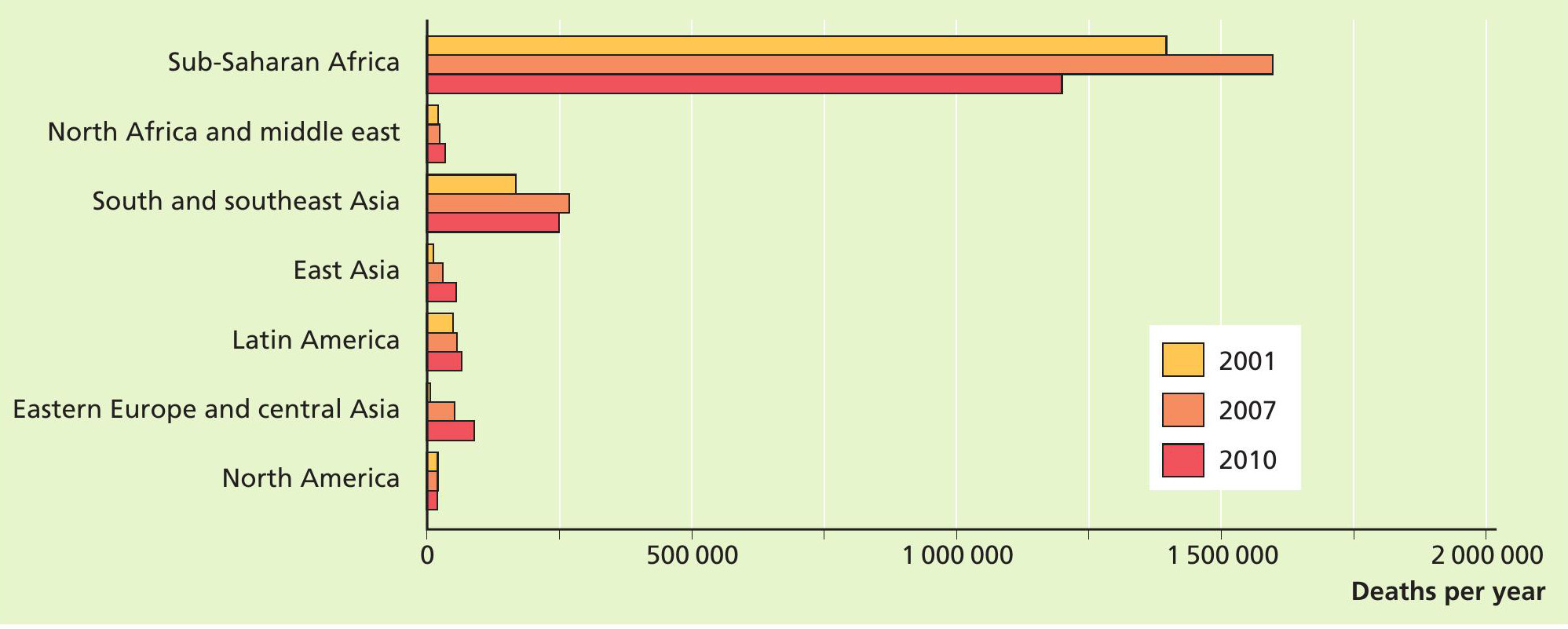
HIV infection/AIDS is a disease of the immune system that is transmitted predominantly through sexual intercourse. In 2010, it affected more than 34 million people worldwide and is considered to be a major health problem in many parts of the world, especially sub-Saharan Africa and south Asia. There is currently no cure for the disease, which resulted in almost 2 million deaths in 2010 (see Figure 1).
In developed countries the disease is controlled using antiviral therapy, which usually inhibits key enzymes important for viral replication. A variety of drugs that target different stages in the virus life cycle must be taken in combination for the therapy to be effective. Antiviral therapy in developing countries is less widespread owing to its high cost and the complexity of the treatment regimes.
Your organisation does not have access to this article.
Sign up today to give your students the edge they need to achieve their best grades with subject expertise
Subscribe




